Telehealth
The use of Telehealth skyrocketed in 2020. Fueled by the COVID-19 pandemic, Telehealth claims rose over 2900% through September of 2020, rising from 0.16% of all claims lines to over 5%. Lest you think telehealth was a new paradigm begrudgingly accepted by patients, consider that customer satisfaction for telehealth visits has been surprisingly high, 86% in a recent JD Power survey, making it far more than a passing fad or a constraint due to the pandemic. This implies that for certain types of clinical visits, telehealth is likely here to stay alongside in-person clinical care. Truth is, a lot can be accomplished remotely with the combination of real-time video, photos, self-testing and clinician/patient remote interaction, and patients have rapidly recognized the value, time savings and convenience, which brings us to the next trend.
AI-driven diagnostics
As more visits become remote, perhaps you may not always need a clinician. Not that we will ever lose the need for doctors, but more health diagnoses may occur via AI analysis. It turns out AI is very effective at examining X-rays, CT scans, dermatology photos and other conditions that rely on image analysis. Recent studies prove that AI-based diagnostic systems and radiologists are able to diagnose conditions with the same confidence interval with results on par with healthcare professionals. Picture yourself for a minute talking to an automated virtual clinician to upload a few images that are sent to outside labs for AI processing, and you have a sense of what the next phase of virtual healthcare may look like, all of which brings us to our next trend.
Enhanced security and integrity for ePHI
As you may have guessed, the prior two trends do come at a cost. The security and integrity of the growing amounts of digital information shared between patients and providers remain of paramount importance. In the US, HIPAA regulations mandate both data integrity and data security requirements for electronic protected health information (ePHI). Whether it’s photos and videos from a remote clinical visit, data gathered from wearable devices or images sent for AI analysis to outside labs, it is critical to guard against hacks, breaches, manipulations and fraud, particularly in today’s world that has rapidly expanded outside of the closed clinical settings.
From a cybersecurity perspective, the security endpoints now include a patient’s home and external labs that use AI for intelligent image analysis. Consider that the number of healthcare breaches reported in the US, for over 500 records, has risen from 18 in 2009 to 642 in 2020, affecting over 268 million records, a staggering number. What can be done to curtail the risk, in light of these advancements?
The shift to telehealth and AI-based external laboratories calls for a new process to protect ePHI from the point of capture throughout its lifecycle. Consider the case of an image, which may originate from the comfort of someone’s home. A patient may send the image to a provider who in turn sends it to outside labs for diagnosis, using advanced AI. For ePHI which typically remains in a clinical setting, that is quite a journey. What can be done to better secure this process? Here are two suggested enhancements:
- Implement security and data integrity from the point of image capture: Ensure that the image is valid from the point of capture, verifying time, date and location. At the same time create a chain of custody that can be followed from the image creation, to storage in a medical record, all the way to the point of archive<
- Use technology such as de-identification to minimize the risk of data breach when the data is sent externally for AI processing or used for purposes such as training AI systems
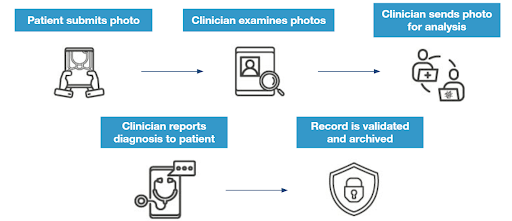
How can this be done? It so happens that technologies, such as blockchain, are particularly adept at maintaining chain of custody of medical data and, if implemented securely, can do so without storing any private or protected health information on the blockchain. Furthermore, AI can automate the de-identification of images before they are sent for external analysis to minimize the risk of breach.
Ultimately, a scalable solution that verifies the validity of data throughout the lifecycle and secures patient information may be a worthwhile investment. If you are looking to embrace the newest trends in healthcare and upgrade your security process to protect critical data, let us know.







